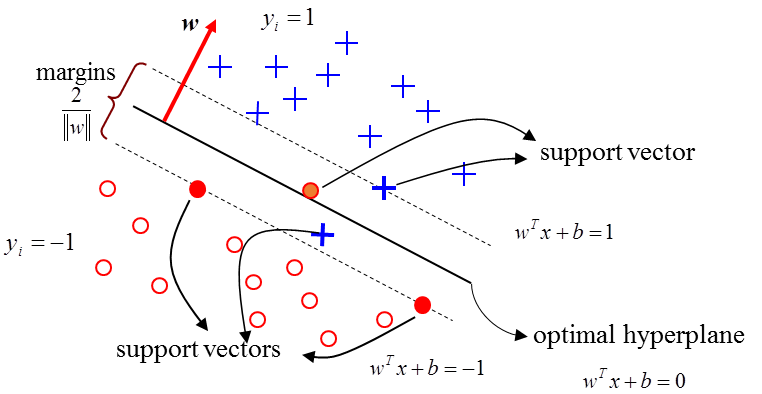
SVM是一種監督式的學習方法,它的基礎的概念非常簡單,就是找到一個決策邊界(decision boundary)讓分類之間的邊界(margins)達到最大,將資料完美分開。
下面圖中有三條直線,都可以將這兩組資料做完美的分割,但綠色直線,特別完美地將這組資料做分割,因為藍色線及紅色線都離這些資料點太近。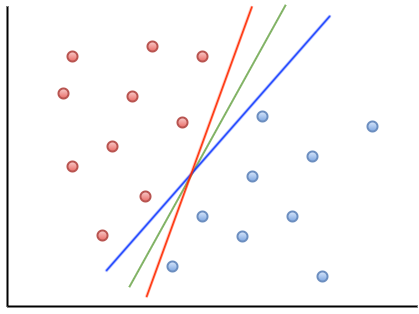
SVM數學推導
兩向量做內積,其意義為把其中一向量投影至另一向量上。以下面這張圖所示,我們把向量v投影至向量u(如果有修過離散數學或工程數學這應該很好理解),p就是我們投影到另一個向量上的長度。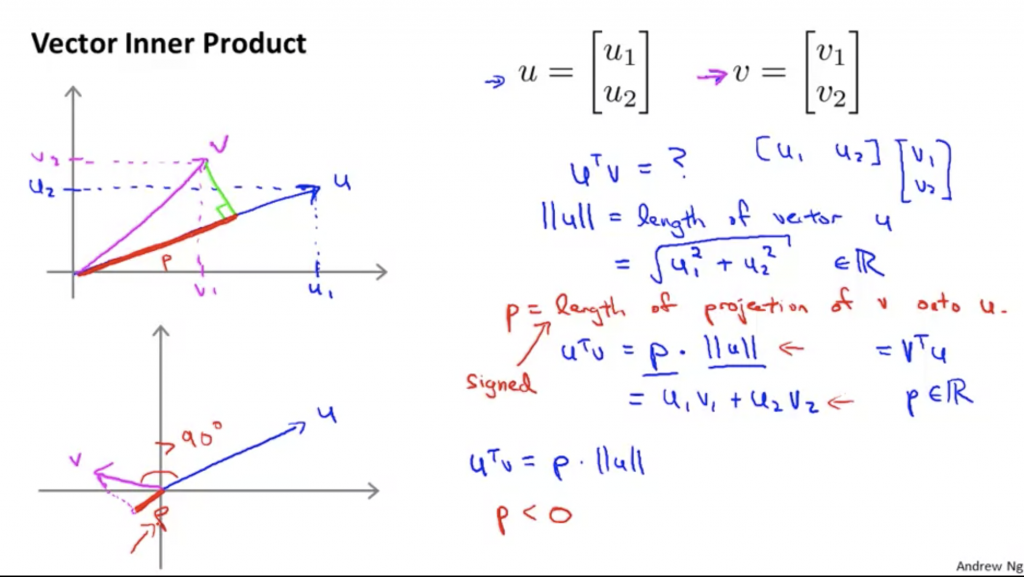
我們要優化的目標函數為1/2θ²(因為採用吳恩達老師教學影片,θ就是大部分書籍裡的w),這邊以向量內積來解釋θ^Tx,也就是把x投影至向量θ上。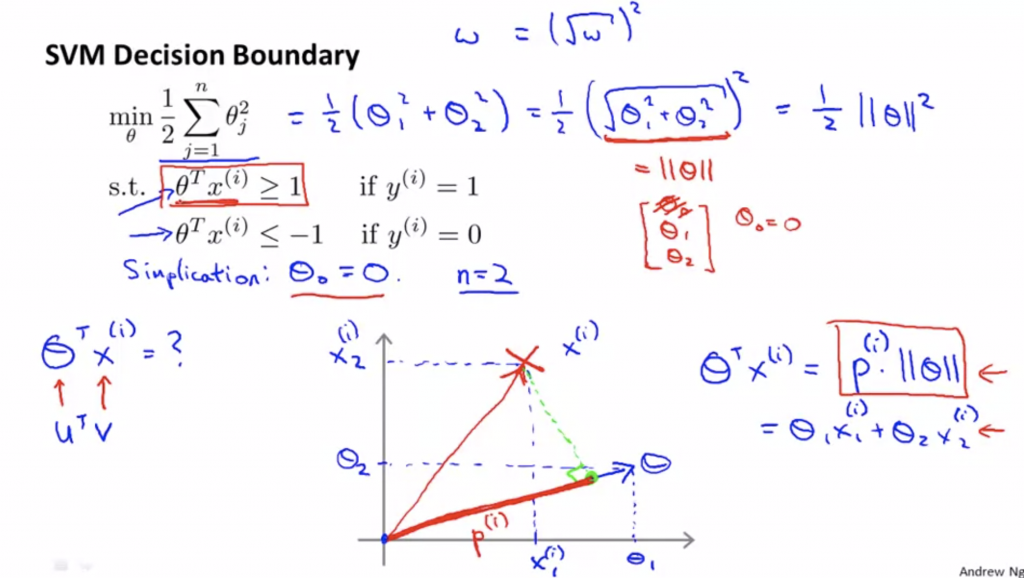
下面這張圖可以看到,左邊的x投影到向量θ上,產生的p非常小,所以會造成θ的範數(長度的概念)非常大,這與我們要優化的目標函數產生矛盾;反之,右邊的x投影到向量θ上,產生的p非常大,所以會造成θ的範數(長度的概念)非常小,符合我們的目的,其中左右兩邊最靠近決策邊界的p值就是所謂的margin。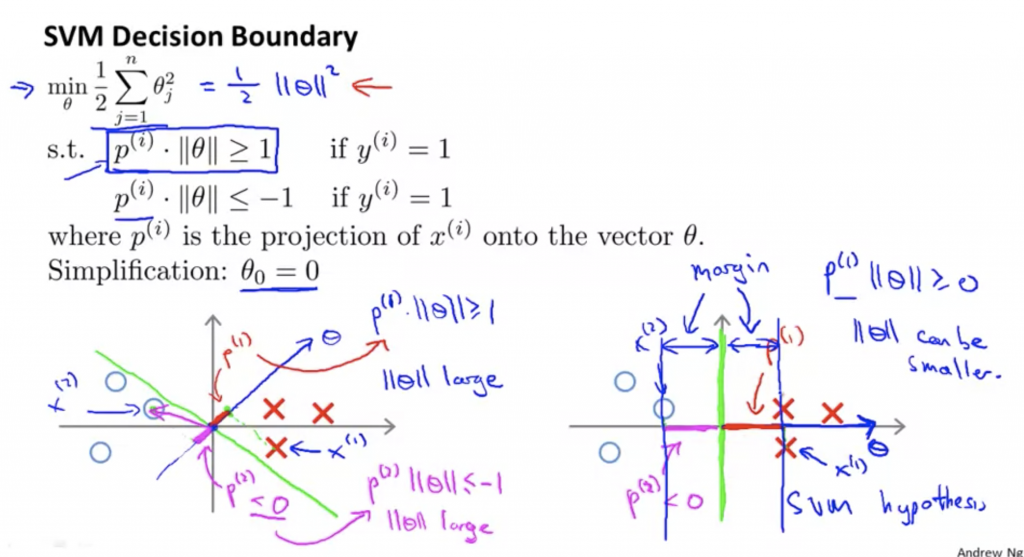
鳶尾花程式碼實作
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import datasets
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, test_idx=None, resolution=0.02):
# setup markers generator and color map
markers = ('s', 'x', 'o', '^', 'v')
colors = ('red', 'blue', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan')
cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))])
# plot the decision surface
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(
np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution),
np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution))
z = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T)
z = z.reshape(xx1.shape)
plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, z, alpha=0.4, cmap=cmap)
plt.xlim(xx1.min(), xx1.max())
plt.ylim(xx2.min(), xx2.max())
# plot all samples
X_test, y_test = X[test_idx, :], y[test_idx]
for idx, cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)):
plt.scatter(
x=X[y == cl, 0],
y=X[y == cl, 1],
alpha=0.8,
c=cmap(idx),
marker=markers[idx],
label=cl)
# hightlight test samples
if test_idx:
X_test, y_test = X[test_idx, :], y[test_idx]
plt.scatter(
X_test[:, 0],
X_test[:, 1],
c='',
alpha=1.0,
linewidth=1,
marker='o',
s=55)
def main():
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data[:, [2, 3]]
y = iris.target
X = np.array([m for m, n in zip(X, y) if n != 2])
boolarr = y != 2
y = y[boolarr]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=0)
sc = StandardScaler()
sc.fit(X_train)
X_train_std = sc.transform(X_train)
X_test_std = sc.transform(X_test)
svm = SVC(kernel='linear', C=1.0, random_state=0)
svm.fit(X_train_std, y_train)
y_pred = svm.predict(X_test_std)
print("Misclassified smaples: %d" % (y_test != y_pred).sum())
print("Accuracy: %0.2f" % accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
X_combined_std = np.vstack((X_train_std, X_test_std))
y_combined_std = np.hstack((y_train, y_test))
plot_decision_regions(
X=X_combined_std,
y=y_combined_std,
classifier=svm,
test_idx=range(50, 100))
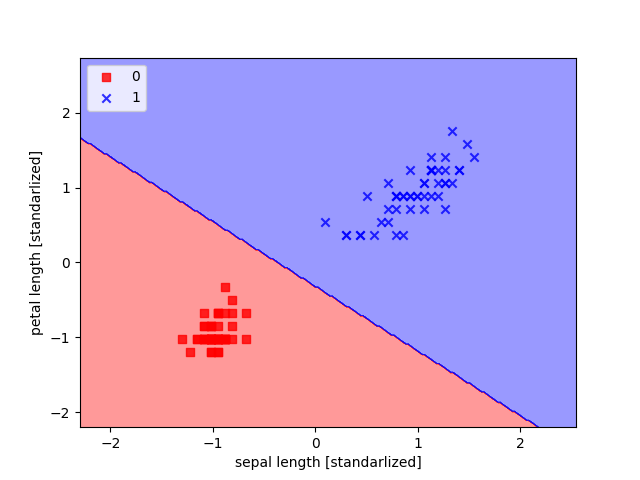
plt.xlabel('sepal length [standarlized]')
plt.ylabel('petal length [standarlized]')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()